Managing Cardiovascular Risks Associated With Prostate And Breast Cancer
Hormone Therapy is a highly effective way to treat various cancer forms, especially Prostate Cancer and Breast Cancer. Despite their effectiveness, however, these treatments come with their long-term risks. The American Heart Association recently provided a statement regarding these risks in Circulation: Genomic and Precision Medicine.
For example, HRT Regimens designed to treat Prostate/Breast Cancer also increase the chance of dangerous cardiovascular dangers such as stroke and heart attack. According to the American Heart Association, these risks can be significantly mitigated with sufficient awareness and preliminary evaluation.
This report offers updated information regarding the complications associated with various forms of Hormone Therapy. The report is designed to help medical specialists treat cancer effectively while managing the downstream risks associated with Hormone Replacement Therapy.
Breast and Prostate Cancer Treatments Improving
Breast Cancer is the most common cancer in the United States, accounting for 30.3% of cancers in women. Prostate cancer is the most common among  males, at 21.5% of all male cancer diagnoses. Aside from skin cancer, most common cancers are associated with hormones.
males, at 21.5% of all male cancer diagnoses. Aside from skin cancer, most common cancers are associated with hormones.
As cancer therapies become more advanced, fewer patients succumb to cancer itself. In fact, cardiovascular disease is the leading mortality risk among those patients under HRT Treatment for hormone-dependent cancer.
Common Treatments for Breast and Prostate Cancer
Three of the most common Endocrine Treatments for cancer are Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulators, Aromatase Inhibitors, and Androgen Deprivation Therapy: SERMs are designed to eliminate tumor development by preventing cancer cells from feeding off of Estrogen.
These treatments allow Estrogen to act generally in other parts of the body like liver/bone tissue without acting on breast tissue.
Two common SERMs are ralloxifene and tamoxifen. Aromatase Inhibitors suppress estrogen production and are commonly prescribed to women after menopause, especially in high-risk patients.
Letrozole, anastrozole, and exemestane are prominent examples of Aromatase Inhibitors. Androgen Deprivation Therapy refers to treatments designed to treat prostate cancer by cutting off access to the fuel source of Testosterone.
This category is broader. Some prescriptions block Testosterone from Prostate Cancer Cells (and prostate cells). Another option includes medications that suppress the hypothalamic/pituitary activity, which triggers Testosterone production.
Cardiovascular Complications Associated with Cancer Treatment
Unfortunately, all the treatments above can negatively affect the cardiovascular system. For example, Aromatase Inhibitors can increase heart attack and stroke risk, and Tamoxifen can lead to blood clots. Because cancers can become resistant to specific treatments, sometimes patients have to change therapies for the best results against cancer.
Unfortunately, while this improves cancer outcomes, it increases the odds of cardiovascular problems, including blood clots, arrhythmia, and high blood pressure. In men, Androgen Deprivation Therapy causes them to experience the whole gamut of issues associated with Low-T, including impaired 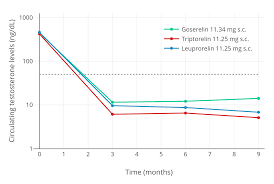 glucose metabolism, increased body fat, and heightened triglyceride/cholesterol levels.
glucose metabolism, increased body fat, and heightened triglyceride/cholesterol levels.
For all of the above treatments, the longer a patient is on the regimen, the greater the risks associated with the therapy. Researchers are investigating exactly how duration impacts risks.
HRT Therapy for Cancer was riskiest for patients diagnosed with heart disease and those with multiple risk factors (including a history of stroke/heart disease, smoking, high cholesterol, obesity, and high blood pressure).
The American Heart Association published this report to help doctors and patients understand the risks associated with Prostate/Breast Cancer Treatment and the cardiovascular precautions that should be taken to maximize patient outcomes.
Shortly, there will hopefully be official guidelines to help doctors navigate the heart risks associated with HRT-Based Cancer treatment. Any patient that could benefit from Hormone Therapy for Cancer should first be directed to a cardiologist for testing and consultation.
- Six Questions You Should Ask Yourself Before Your Trip To The Doctor [Last Updated On: August 22nd, 2024] [Originally Added On: October 16th, 2020]
- Requirements For Hormone Replacement Therapy [Last Updated On: January 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 17th, 2020]
- Hgh Testimonials And Reviews [Last Updated On: January 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 18th, 2020]
- Clomiphene Citrate Information And Guide [Last Updated On: August 25th, 2024] [Originally Added On: October 19th, 2020]
- Breast Cancer: Separating Fact From Fiction [Last Updated On: January 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 20th, 2020]
- A Brief Guide To Endocrinology [Last Updated On: July 26th, 2024] [Originally Added On: October 21st, 2020]
- Presence of Specific Genetic Allele Influences Response to Growth Hormone Therapy [Last Updated On: July 4th, 2024] [Originally Added On: July 15th, 2021]
- Macimorelin A New Diagnostic Tool for Diagnosing Adult Growth Hormone Deficiency [Last Updated On: June 28th, 2024] [Originally Added On: July 22nd, 2021]
- Ipamorelin Acetate with CJC 1295 for HGH Deficiency [Last Updated On: February 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: May 29th, 2022]
- Why Do My Friends Feel So Good While I Feel So Bad? [Last Updated On: March 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: June 20th, 2022]
- My Vacations Weren’t Vacations Anymore [Last Updated On: March 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: June 28th, 2022]
- Racing Ferraris – A Stressful Way to Earn a Living [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: July 12th, 2022]
- Symptoms of Growth Hormone Deficiency in Adults [Last Updated On: July 7th, 2024] [Originally Added On: September 15th, 2022]
- HGH and Intellectual Improvements [Last Updated On: July 21st, 2024] [Originally Added On: March 8th, 2023]
- Abie’s Lies [Last Updated On: July 13th, 2024] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2023]
- Revolutionizing the Silver Years: Age-management Warriors Defying Time’s Grip [Last Updated On: February 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 14th, 2025]
- Introduction: A Personal Story [Last Updated On: February 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 18th, 2025]
Word Count: 596







