Subcutaneous Injection Procedures
Subcutaneous Injection information and Procedures
Both HGH and Testosterone Hormone Replacement Therapy can be provided via injection. The only safe and effective way to administer Therapeutic Human Growth Hormone is with a shot.
On the other hand, testosterone can be delivered via several different means, including Testosterone gel, Testosterone Creams, Testosterone Sprays, and even implanted Dermal Pellets. 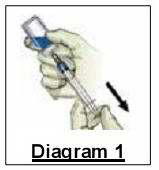
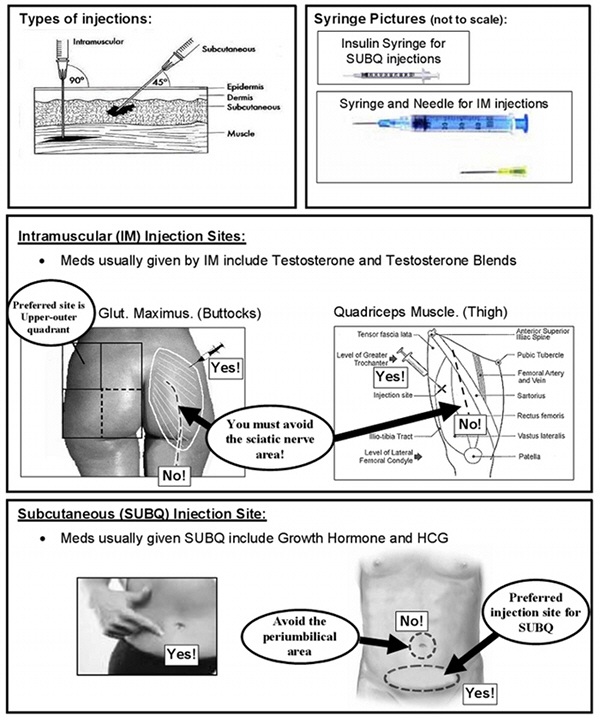
Although both forms of medication can be delivered via injection, they are delivered via different techniques. Human Growth Hormone is delivered using a technique known as Subcutaneous Injection. Testosterone is almost always delivered via Intramuscular Injection.
What is a Subcutaneous Injection?
A Subcutaneous Injection is a form of injection delivered just under the layers of the skin. The scientific shorthand, SubQ, sometimes refers to subcutaneous Injections. This injection form utilizes a short, thin needle specially designed to puncture just below the skin.
The medication contained within the syringe is delivered to the space between the most profound skin levels and the muscle tissue's top layers. The needle used for Subcutaneous Injection is often referred to as an Insulin Needle because it is the type of needle used by diabetics to deliver daily Insulin shots.
What Kinds of Medicine Can Be Delivered Subcutaneously?
Many types of medicine cannot be administered orally. Human Growth Hormone is one example of this. Insulin is a second example. These medications cannot survive the digestive process because enzymes and acids in the stomach are designed to tear apart complex proteins, hormones, and enzymes, rendering them to their component parts.
Usually, this is a good thing. The stomach has to break apart the food you eat to its essential components so that the organs of your body can reassemble those nutrients to serve the purposes of your body.
Complex organic medications are different, however. These delicate medications must be delivered to target organs intact so they can be appropriately activated.
Why Are Subcutaneous Injections Superior to Intravenous Injections?
Although it is also possible to deliver medications intravenously, in many cases, it is preferable to deliver them in other ways. Intravenous Injections take a certain level of skill and finesse to deliver quickly and efficiently. To deliver a medication intravenously, it is necessary to target and hit a vein perfectly to direct the contents of the needle directly to the bloodstream.
On the other hand, subcutaneous injections are much easier to deliver, as they simply need to be delivered just under the skin's surface. There is a chance that you will nick a blood vessel when you deliver medication subcutaneously, but if you do so, all you have to do is pick another injection site. Subcutaneous Injection is ideal for delivering minimal doses of potent medications.
Subcutaneous Injection is convenient, safe, and highly effective.
Subcutaneous Injections are ideal for drug doses up to two milliliters. Human Growth Hormone Injections for Adult HGH Deficiency generally range from 1-2 CCs. Subcutaneous Injections are relatively fast-acting but still take a little while to metabolize by the body thoroughly.
Generally, Subcutaneous Injections deliver medications over the course of a twenty-four-hour period.
What Types of Medicine are Administered Subcutaneously?
Because of the small maximum volume for Subcutaneous dosage, medications that utilize this delivery form tend to either be incredibly potent or only needed in small doses. Protein-derived medications are often delivered subcutaneously because they would not survive ingestion due to the powerful acids within the stomach.
Hormones, derived from proteins, are the second example of a medication that is often delivered Subcutaneously.
As we mentioned earlier, Subcutaneous injections are delivered with the same needle diabetics use to deliver Insulin. Human Growth Hormone is also administered in the same fashion. Subcutaneous Injection is also helpful for medications that need to be delivered rapidly but are effective in small doses.
Epinephrine is an example of a medication delivered subcutaneously quickly in emergencies. Epinephrine injections are generally stored in "pens" that can be activated and used quickly because Epinephrine is used to treat dangerous allergic reactions, such as those that individuals have for substances such as peanuts and poison from bees stings.
These Epinephrine Pens are called EpiPens, and you likely know multiple people who carry them daily. A number of pain meds can also be delivered Subcutaneously, even potent ones such as hydromorphone and morphine. 
Certain powerful anti-nausea medications can also be delivered through an insulin needle, such as dexamethasone and metoclopramide. Allergy shots and some vaccines are delivered utilizing this method, although others are delivered Intramuscularly.
Subcutaneous Injections also have applications for many drugs which can be delivered orally, but the patient cannot take drugs by mouth.
How Are Subcutaneous Injections Administered?
When administering a subcutaneous injection, it is essential to choose an appropriate injection site for maximum safety and effectiveness. For Subcutaneous Medications to work appropriately, they must be delivered just underneath the skin. Although all areas of the body contain this subcutaneous layer, some parts of the body have more to work with than others.
Where Are the Best and Worst Locations To Administer a Subcutaneous Injection?
Choosing a location where this sub-dermal area is clear is crucial because it is essential to avoid hitting blood vessels, bone, or muscle with the needle. The most ideal areas of the body for Subcutaneous Injection are the stomach, the front of the thigh, or the sides or back of the upper arm.
What Type of Needles Are Used in Subcutaneous Injections?
Subcutaneous injections are delivered using needles that are 5/8 inch long. The needle-width is generally relatively small, usually 25 or 27 gauge. Doses between one and two milliliters may require a slightly wider needle.
How Are Subcutaneous Medications Stored?
Most Subcutaneous Medications store the medication as a liquid in small vials. However, certain drugs, such as Human Growth Hormone, are stored differently. For susceptible and delicate drugs like HGH, pharmacies and medical manufacturers convert the drug to a powder form through a process known as Lyophilization.
This simply means the medication is freeze-dried until it is ready to use. The Lyophilization process is safe to use on delicate medications like Human Growth Hormone and does not alter or break down the chemical structure of the medication.
Liquid HGH is incredibly sensitive to both temperature and tampering. It must be stored under refrigeration, even when lyophilized, and even agitating the vial too much can break down the dried HGH and render it inert.
Lyophilized medications like Human Growth Hormone are prepared for Subcutaneous Injection through a process known as Reconstitution. This is performed carefully by combining the Lyophilized medication with a sterile solution to restore it to its standard composition.
Simple, sterilized water will be sufficient for medications that will be used relatively quickly after reconstituting.
For other drugs, including Human Growth Hormone, intended to be stored up to a month after reconstitution, the Lyophilized Medication is generally combined with water treated with a preservative such as benzene.
Some medicine vials are only intended to be used once, whereas others are intended for multiple uses.
Subcutaneous Injection with Pens
Almost all Subcutaneous Injections can be delivered using a standard insulin needle and syringe. Still, other products are intended to make the injection process more accessible and straightforward.
The most common of these is the "Pen." Pens are small machines that store and deliver medication quickly and are shaped like a pen. The pen contains liquid medication, and it uses a new needle each time it is delivered.
These pens are generally engineered to automatically deliver a range of doses simply by adjusting a dial. Some medications can also be delivered via computerized, hand-held devices.
Subcutaneous Injection Walkthrough
When preparing to administer a subcutaneous injection, the first thing you do is wash your hands thoroughly. If you deliver a subcutaneous injection for someone else, it is critical to wear gloves.
In addition to washing your hands, you should also appropriately sterilize the area where you plan to arrange your supplies. Maintaining optimal cleanliness throughout the injection process is crucial to minimize the potential for contamination.
The following steps are necessary when performing Subcutaneous Injections utilizing a syringe:
Make Sure the Right Person is Getting the Right Medication
Before drawing the medicine from its vial, always look at the bottle to ensure that you constantly inject the appropriate medication. Nurses and other medical professionals constantly stress the importance of the 5 Rights of Medication Delivery: the Right Medicine, the Right Dosage, the Right Patient, the Right Time, and the Right Route.
Following these five steps every time, ensures that the treatment you intend to deliver is delivered appropriately and effectively.
After you have obtained the appropriate vial of medication, remove the cap and place it to the side. If the pen or vial you are using is intended for multiple uses, write down the date you first opened the vial.
After being opened, Subcutaneous Medications often have relatively short shelf lives. For example, once reconstituted, Human Growth Hormone Replacement Therapy generally keeps for a few weeks. After that point, it is no longer medically potent.
Draw the Medication from the Vial
After removing the cap from the medication, sterilize the rubber stopper on the vial with an alcohol swab. At this point, take your syringe and pull the plunger back so that the amount of air inside represents the dose that you intend to draw. At this point, carefully remove the cap covering the tip of the needle, making sure not to make contact with it.
If you accidentally touch the needle, discard it and choose another needle.
 Slowly bring the needle into contact with the stopper of the vial. After piercing the vial with the needle, inject the air contained within the needle into the vial. This will maintain air pressure in the vial and make it easier to draw the medication.
Slowly bring the needle into contact with the stopper of the vial. After piercing the vial with the needle, inject the air contained within the needle into the vial. This will maintain air pressure in the vial and make it easier to draw the medication.
At this point, tilt both syringe and vial topside down with the needle pointed straight upward. If there are air bubbles in the solution, tap the side of the vial lightly to jar any air bubbles to the bottom of the upturned vial.
Draw back the plunger until the dose you intend to inject is contained within the vial. Carefully pull the needle from the vial and check the syringe for any trapped air bubbles. If there are any bubbles of air, tap the syringe lightly so that they rise to the top.
At this point, slowly depress the plunger, ejecting any bubbles contained within. Release the plunger when you see the medication itself breach the tip of the needle.
If Administering Subcutaneous Medication using a Pen:
As we mentioned earlier, Injection Pens are used because they simplify the process significantly. When using a Pen, the medication is already contained within the device and ready for use. You only need to replace the needle every dose until either the pen is expended or the medication contained within is out of date.
Make sure that the needle is connected to the pen safely without contacting the tip of the needle. When using a Subcutaneous Pen, the dial on the pen's side represents the dose size that will be delivered.
Turn the dial so that the pen will deliver the appropriate dose when activated.
Preparing the Injection Site:
When choosing a location on your body to deliver the medication, we recommend one of the sites mentioned above: the midsection, the sides or back of the upper arms, or the top of the thighs. When selecting a location, pick a spot of clean and healthy skin. Avoid injecting into an area with skin irritation, burns, bruising, hardness, or swelling. 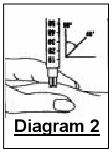
Also, injecting into a different location every time you deliver a shot is essential. Repeatedly injecting in the exact location can weaken the skin or cause irritation and pain. Before settling in for your injection, clean the injection site with an alcohol swab. Set the syringe or pen to the side where it can be picked up and utilized efficiently.
With one hand, take the patch of skin, and squeeze it between your index finger and thumb so that it is raised. This allows the needle to inject entirely into the skin while delivering the medication to the appropriate layer underneath the skin. Pick up the needle and hold it right to the skin.
If you have low body fat, you may need to turn the needle to a forty-five-degree angle to inject the medication correctly.
Performing the Subcutaneous Medication
When ready, pierce the skin firmly and steadily with the needle. When the needle is fully inserted into the skin, draw back a little. If you draw blood when you pull the plunger back, you have pricked a blood vessel and will need to pull out, replace the needle, and choose a new injection site. If you do not see any blood, deliver the medication by depressing the plunger slowly and thoroughly.
After you have delivered the medication, pull the needle out of the skin quickly yet carefully. After removing the needle, set the syringe or pen aside and clean the injection site with clean gauze. There should be very little blood if you experience bleeding after the injection. Do not be overly concerned if you occasionally experience bruising due to the injection.
Dispose of All Equipment Appropriately
After you have completed the injection process, recap your needle and throw it away in an OSHA-Approved SHARPS container. If you do not have a SHARPS container or other container approved for medical waste, do not inject until you have a way to dispose of the needles safely. Used needles are bio-hazardous waste, and it is dangerous and illegal to dispose of them improperly.
What Complications are Related to Subcutaneous Injection?
With any injection, there is a non-negligible chance that you will experience an infection. Although there is always a risk of infection, this risk can be reduced significantly by following procedures that ensure that all aspects of injection are handled appropriately and cleanly.
Even when you follow all of the appropriate steps for safe injection, you may still experience changes in the skin, irritation, or bruising. Changing injection sites with every administration will significantly reduce the risk of experiencing these symptoms.
Patients with cardiovascular circulation may have issues experiencing the full effects of Subcutaneous Medication because poor circulation inhibits optimal absorption rates.
Some patients may also be allergic to preservatives in medications intended to increase the shelf life of more extensive prescriptions. For these patients, alternative preservatives may be needed, or the patient may opt for smaller vials that do not require preservatives.
The information in this document is provided for informational purposes and is not meant to substitute for the advice provided by your physician or another medical professional. You should not use the information contained herein to diagnose or treat a health problem or disease or prescribe any medication. If you have or suspect a medical problem, promptly contact your health care provider or representative.
Reference
- What Is Male Hypogonadism? [Last Updated On: December 22nd, 2024] [Originally Added On: July 18th, 2020]
- What Is Low-t And How Can It Effect My Life? [Last Updated On: September 20th, 2024] [Originally Added On: July 22nd, 2020]
- Identification Of Late Onset Hypogonadism In Middle Aged And Elderly Men [Last Updated On: October 21st, 2024] [Originally Added On: July 24th, 2020]
- Importance Of Hormone Balance For A Man's Health [Last Updated On: September 18th, 2024] [Originally Added On: July 25th, 2020]
- Genetics And Gene Therapy. What Are Genes? [Last Updated On: September 15th, 2024] [Originally Added On: August 2nd, 2020]
- Whey Protein [Last Updated On: September 13th, 2024] [Originally Added On: August 3rd, 2020]
- Hormone Replacement Therapy Blood Testing [Last Updated On: September 14th, 2024] [Originally Added On: August 7th, 2020]
- Gh-rh [Last Updated On: September 6th, 2024] [Originally Added On: August 12th, 2020]
- How Does Growth Hormone Testing Work? [Last Updated On: February 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: August 15th, 2020]
- Important Figures In Hormone Replacement Therapy Research [Last Updated On: August 16th, 2024] [Originally Added On: August 16th, 2020]
- Certified Age-management And Longevity Professionals [Last Updated On: February 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: August 28th, 2020]
- Bio-identical Genotropin Hormone Replacement Therapy [Last Updated On: August 6th, 2024] [Originally Added On: September 4th, 2020]
- HGH Injections [Last Updated On: February 28th, 2023] [Originally Added On: March 7th, 2021]
- Growth Hormone Injection Treatment For Women [Last Updated On: February 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 8th, 2021]
- Buy Growth Hormone Injection Treatment For Men [Last Updated On: February 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 9th, 2021]
- The Conscious Evolution Institute For Quality Hormone Replacement Therapy [Last Updated On: October 29th, 2024] [Originally Added On: March 10th, 2021]
- 25 Foods That Can Improve Your Health [Last Updated On: October 28th, 2024] [Originally Added On: March 11th, 2021]
- Change Your Life With A Conscious Evolution Lifestyle [Last Updated On: February 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 12th, 2021]
- Understanding The Various Causes Of Human Obesity [Last Updated On: February 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 13th, 2021]
- Male Hormone Replacement Therapy Blood Panel [Last Updated On: February 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 15th, 2021]
- Getting Started With Hormone Replacement Therapy [Last Updated On: February 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2021]
- Buy Female Blood Diagnostics [Last Updated On: October 25th, 2024] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2021]
- Low Testosterone and other Sex Drive Killers that Cause Low Libido in Men [Last Updated On: February 14th, 2025] [Originally Added On: May 1st, 2022]
- The effects of Human Growth Hormone (HGH) on the skin [Last Updated On: February 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: May 8th, 2022]
- Testicle Tanning – See Through the Hype [Last Updated On: February 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: May 30th, 2022]
- Lean Muscle Mass Critically Important to Healthy Aging [Last Updated On: February 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: June 28th, 2022]
- Can Vitamin B6 Help Relieve Anxiety? [Last Updated On: February 14th, 2025] [Originally Added On: August 2nd, 2022]
- A Chemical Found in Common Household Items May Disrupt a Hormone Necessary for Healthy Pregnancy [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: August 2nd, 2022]
- Matching Libidos Ensure Healthy Relationships [Last Updated On: March 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: December 11th, 2022]
- How Fluctuating Libidos Affect Aging Men and Women [Last Updated On: February 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: January 10th, 2023]
- Adopting a Conscious Evolution Lifestyle for Improved Health and Longevity [Last Updated On: February 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 9th, 2025]
- Male Hormone Replacement Therapy: Diagnostic Blood Test Regime [Last Updated On: February 14th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 13th, 2025]
- Unleash the Power of Vitamin B6: The Natural Antidote to Anxiety! [Last Updated On: February 14th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 14th, 2025]
- The Impact of Human Growth Hormone Deficiency in Men [Last Updated On: February 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 15th, 2025]
- Maintaining Lean Muscle Mass: A Crucial Facet of Healthy Aging [Last Updated On: February 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 15th, 2025]
- Introduction to Testicle Tanning [Last Updated On: February 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 16th, 2025]
- Introduction to Hormone Replacement Therapy [Last Updated On: February 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 17th, 2025]
- Importance of Matching Libidos for Healthy Relationships [Last Updated On: February 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 19th, 2025]
Word Count: 2517







