Estrogen Hormone Replacement Therapy May Diminish Alzheimers Disease Risk

Estrogen Hormone Replacement Therapy May Diminish Alzheimer's Disease Risk
What is Alzheimer's?
Alzheimer's disease is the most diagnosed form of dementia in the world. As of yet, there is no cure for the disease, but researchers worldwide spend their entire careers attempting to discover ways to alleviate or even cure the syndrome.
Our knowledge of the disease grows more quickly by the year, and there is significant hope that our world's greatest minds will discover a means to defeat this dreaded degenerative condition within the coming generation.
Alzheimer's develops in a different pattern and at a different speed for every patient, but the common symptoms are:
- Increased aggression and irritability
- High levels of confusion and disorientation
- Rapid changes in mood
- Atrophy of language ability
- Long-term and eventually short-term memory loss

- In later stages, a loss of physiological control, in which, over time, the patient is eventually wholly dependent upon a caregiver.
There are three primary hypotheses regarding the cause of Alzheimer's:
Cholinergic Hypothesis:
This was the original hypothesis regarding Alzheimer's, and treatment approaches using this theory as a starting point produce only minimal beneficial effects.
This hypothesis predicts that Alzheimer's disease is primarily the result of a reduced ability of the brain to synthesize acetylcholine.
Tau Hypothesis:
This hypothesis centers around the idea that abnormalities in a particular type of protein known as Tau Protein can cause the effects of Alzheimer's disease.
It is hypothesized that hyperphosphorylated tau interacts with other forms of tau protein, creating clumps of protein known as neurofibrillary tangles inside nerve cells. These tangles disrupt the function of nerve cells, clogging up the active transport system and preventing neuronal messages from 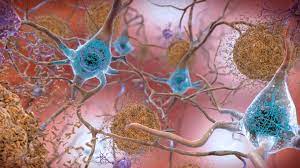 reaching target destinations.
reaching target destinations.
At first, this leads to misdirected neuron firing but can eventually lead to the neurons' death.
The Amyloid hypothesis
The Amyloid Hypothesis is the most widely researched and studied hypothesis and is the hypothesis to which the research discussed in this article is related. According to this hypothesis, Alzheimer's is primarily caused by the formation of Beta-Amyloid deposits in the brain, which clogs up neuronal pathways, leading to the detrimental effects of the disease.
One of the primary reasons this hypothesis carries so much weight is that individuals who display an increased proclivity for forming these proteins display a significantly increased risk of the disease. Individuals with Down syndrome have three copies of this genetic abnormality, and as a result, these patients display symptoms of Alzheimer's at an age as early as 40.
New Study: APoE4 Precursor for Alzheimer's and Advanced Aging
Endocrinologists have made a number of discoveries regarding the effect of Estrogen Replacement Therapy on Alzheimer's, and New clinical research provides evidence that Estrogen Hormone Treatments may be able to slow down the process of aging in middle-aged females who are at increased risk of Alzheimer's disease.
In this clinical study, otherwise healthy female patients who were going through menopause while also harboring a genetic increased risk of Alzheimer's did not succumb to the disease when treated with Hormone Replacement Therapy.
The genetic abnormality APoE4 has been linked to processes that speed up the natural aging process in women. Hormone Replacement Therapy featuring Estrogen may counteract the detrimental effects of this genetic condition and help older women avoid the ravages of Alzheimer's disease .
.
What is APoE4?
AP0e4 is the most vital causal genetic link for developing Alzheimer's disease. This gene is responsible for producing an enzyme known as Apolipoprotein E Type 4. Macrophages and the liver primarily release Apolipoprotein E to break down triglycerides.
Ap0E4 performs this function but is also correlated with creating devastating protein abnormalities in the brain, which lead to Alzheimer's. Those who carry 2 copies of the Ap0E4 gene have a ten to thirty times increased likelihood of developing Alzheimer's disease.
Ap0E4 is so strongly correlated with Alzheimer's disease that James Watson, one member of the duo of scientists who first discovered the existence of DNA, refuses to be tested for the genetic abnormality.
Individuals with an active Ap0E4 gene have a 90% chance of developing Alzheimer's by age eighty without treatment. Although Alzheimer's research is incredibly active, there are still more questions than answers regarding this devastating disease.
APoE4 Slowly Degrades the Body
According to Dr. Natalie Rasgon, ApoE4 affects women at the cellular level long before these changes affect the body to a noticeable extent, increasing the physiological age of the cells long before this aging process becomes apparent and symptomatic. Dr. Rasgon is a behavioral science and psychiatry professor at the Stanford School of Medicine in California.
This new study provides further evidence that Estrogen Replacement Therapy may be able to shield many older women from the effects of Alzheimer's disease, especially those who harbor this critical gene.
One of a Number of Studies Linking APoE4 to Alzheimer's
There have been a number of previously conducted studies that have shown that ApoE4 likely plays a role in Alzheimer's disease and general cognitive decline as a result of the aging process.
In another similar study, not directly related to ApoE4, 472 female patients were followed for 16 years. Some of the participants utilized Hormone Replacement Therapy, while others did not utilize the treatment.
Researchers found that patients who used Estrogen and other forms of Hormone Replacement Therapy had an incidence of Alzheimer's, which was fifty percent lower than those patients who did not use the therapy.
This gene is prevalent among Alzheimer's patients and is active in around forty percent of patients afflicted with the disease.
Dr. Rasgon's laboratory group focused primarily on telomeres, caps that close off the ends of chromosomes and are responsible for genetic stability. These telomeres function like genetic fuses over time. Each time a cell reproduces, the telomeres become slightly shorter.
What are Telomeres?
Telomeres are areas of DNA at the ends of chromosome strands and consist of repeating lines of genetic data that are inert. These lines form a cap on the ends of the chromosomes to prevent them from breaking down.
During the process of cell replication, the enzymes that encourage the reproduction of chromosomes cannot perform their function all the way to the very ends of cells, leaving a very brief portion of the chromosome un-copied.
If chromosomes did not have telomeres that featured this inert genetic data, then every time the cells divided, our chromosomes would lose vital genetic 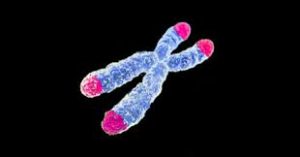 code, and our bodies would deteriorate. These telomeres are partially consumed by the enzymes which encourage cell replication, but other cellular enzymes are responsible for rebuilding telomeres.
code, and our bodies would deteriorate. These telomeres are partially consumed by the enzymes which encourage cell replication, but other cellular enzymes are responsible for rebuilding telomeres.
These cells are known as Telomerase Reverse Transcriptase. Under normal circumstances, telomeres set a soft limit on the natural life spans of animals, including humans. Telomeres play a significant role in the aging process.
Studies such as those performed by Dr. Ragson help us understand more about telomeres and how we can extend our lifespans by manipulating the rate at which telomeres break down.
There is also ongoing research regarding how telomeres can be adequately preserved or even lengthened to extend their lifespan. In many ways, Hormone Replacement Therapy and Telomere Maintenance appear to be related.
Alzheimer's Correlated to Quicker Aging
The current body of scientific knowledge suggests that Alzheimer's and the biological aging process are likely correlated in a large subset of female patients.
If the telomeres reach a specific abridged size, the cells can begin to die off, or in other cases, the cells may lose their ability to continue to divide.
When the cells start to function abnormally due to the aging process, the signs of aging begin to become physiologically apparent on a holistic level. Symptoms of aging such as loss of muscle tone and cognitive sharpness, as well as wrinkled skin, start to manifest, in addition to other adverse side effects which affect every system of the human body.
The rate at which the telomeres shorten is highly variable among individuals. This can be used to accurately measure biological age, which is systematically different from chronological age, affecting each individual at a unique rate that is not entirely dependent upon time.
The researchers studied telomeres sampled from white blood cells drawn from seventy completely healthy women aged between forty-five and sixty-five. All seventy were taking Estrogen Hormone Replacement Therapy.
How Might Estrogen Prevent Alzheimer's?
When menopause begins, estrogen levels decline at a rapid pace. Almost all women are aware of some symptoms, including cold sweats, hot flashes, mood instability, and lapses in memory.
What most women probably do not realize is that menopause can increase the risks of a number of other medical issues as well, including Alzheimer's disease. In the past, a few small-scale studies have suggested that Estrogen Replacement Therapy may be a treatment option for those who suffer from Alzheimer's disease.
Although the benefits of reversing the effects of Alzheimer's with Estrogen Replacement Therapy seem slim, there is growing evidence that Estrogen may be able to prevent the disease or slow its progression, mainly when utilized during the period of Menopause.
These benefits may also persist later in life when Estrogen HRT is utilized in smaller doses.
New studies have also shown that Estrogen provides a number of benefits to the brain in addition to safeguarding it against the threat of Alzheimer's. There has been a significant amount of animal research on the Effects of Estrogen on Brain Cells, and it is apparent that the hormone plays a significant role in protecting and supporting the function of brain cells.
Estrogen Associated with Healthy Acetylcholine Levels
Healthy Estrogen levels are associated with optimal levels of acetylcholine in the brain and are vital to maintaining cognition and memory. Estrogen also apparently can shut down the formation of plaques known as Beta Amyloids, which cause the symptoms of Alzheimer's disease.
Beta Amyloid plaques result from an enzyme abnormality that causes the enzymes to produce malfunctioning proteins which break down the function of the brain, eventually leading to total cognitive breakdown and death.
Although Estrogen alone may not be a proper treatment for active Alzheimer's, there is still promise that Estrogen HRT, when utilized in combination with other forms of Alzheimer's medical treatment such as Aricept (donepezil), may be able to improve health outcomes for patients with Alzheimer's disease.
APoE4 Study Parameters
The seventy women on Estrogen HRT were split into two variable groups. The first group of women stayed on Hormone Replacement Treatments, while the second group stopped all hormone therapy.
 After two years, the participants had their white blood cells drawn a second time, and the scientists measured the rate by which the length of the telomeres shortened.
After two years, the participants had their white blood cells drawn a second time, and the scientists measured the rate by which the length of the telomeres shortened.
Among the healthy patients who halted Hormone Replacement Therapy, those with the active Alzheimer's gene were 6 times as likely to have telomeres that shortened at an abnormally rapid pace than participants who did not have an active Alzheimer's gene.
For these women with the active ApoE4 gene, the telomeres reduced in length at a rate that would normally be expected over a decade rather than two years. Physiologically, these women were aging at a rate five times as fast as those with the deactivated gene.
Estrogen Slows Down Biological Aging Associated with APoE4
Hormone Replacement Therapy featuring Estrogen was shown to alleviate this issue, however. In patients at enhanced risk of Alzheimer's yet remained on Estrogen HRT, telomere length shortened at an average rate which correlated with their cohorts with the deactivated gene.
This is robust evidence that Hormone Replacement Treatments with Estrogen may have the ability to delay or prevent Alzheimer's disease, although much more study is needed to prove the hypothesis.
Professor Rasgon says that this study increases our knowledge of the benefits of Estrogen Replacement Therapy and, in the future, will help us pinpoint exactly which patients are likely to receive the maximum benefit from the hormone treatment.
- Research Hgh For Patients Over 60 [Last Updated On: September 8th, 2024] [Originally Added On: September 30th, 2020]
- Natural Hormone Replacement Abc News 13 [Last Updated On: December 21st, 2024] [Originally Added On: October 2nd, 2020]
- My Own Experience With Human Growth Hormone Case Study [Last Updated On: February 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 3rd, 2020]
- Ipamorelin Alternative To Hgh Injection Therapy [Last Updated On: February 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 4th, 2020]
- Human Growth Hormone Therapy For Adult Hgh Deficiency Do The Benefits Stack Up [Last Updated On: February 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 5th, 2020]
- Human Growth Hormone Rehabilitation Benefits [Last Updated On: September 1st, 2024] [Originally Added On: October 6th, 2020]
- HRT [Last Updated On: August 5th, 2024] [Originally Added On: October 7th, 2020]
- Hormone Replacement Therapy With Pellet Implants [Last Updated On: August 4th, 2024] [Originally Added On: October 8th, 2020]
- Omnitrope Bio-identical HGH Injections [Last Updated On: February 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 9th, 2020]
- Imported Human Growth Hormone Is Illegal In The United States [Last Updated On: February 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 10th, 2020]
- Igf-1 Stimulates The Growth Of Motor Neurons In The Brain [Last Updated On: September 2nd, 2024] [Originally Added On: October 11th, 2020]
- The Potential Benefits Of Estrogen On Alzheimer's Risk [Last Updated On: January 31st, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 13th, 2020]
- Dr. Hotze Talks About A Natural Solution For Depression. [Last Updated On: December 23rd, 2024] [Originally Added On: October 14th, 2020]
- Anastrozole Research Study [Last Updated On: January 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 15th, 2020]
- Symptoms Of Hormonal Imbalance In Women: What To Look For [Last Updated On: March 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: May 12th, 2021]
- Beware of Fake Hormone Booster Pills – Sign Up for the Real Deal [Last Updated On: February 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: December 21st, 2022]
- Chronic Fatigue versus Hormone Deficiency: How Can Patients and Doctors Tell the Difference? [Last Updated On: July 10th, 2024] [Originally Added On: January 18th, 2023]
- Ipamorelin: A Safer, Cost-Effective Alternative to HGH Therapy [Last Updated On: February 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 13th, 2025]
- Treatment of Hormone Deficiencies [Last Updated On: February 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 15th, 2025]
Word Count: 1964







